
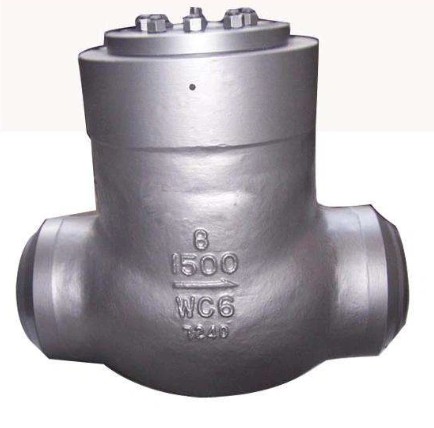
Pressure Seal Bonnet Check Valve
Introduction
Pressure Seal Bonnet Check Valve is designed to handle various operating conditions in the pipeline for industries such as petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, chemical fertilizer, and electric power. It is ideal for clean media like water, oil, steam, and acid mediums, but not suitable for mediums with solid particles and high viscosity. With its ability to handle high-pressure and high-temperature applications, it is commonly used in power generation, oil and gas production and refining, chemical processing, water treatment plants, and petrochemical plants.

Technical Specifications:
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Sizes | NPS 1/2 to NPS 48 |
| Pressure Class | Class 150 to 2500 |
| Casting Materials | A105, A182 F304, F3304L, F316, F316L, A182 F51, F53, A350 LF2, LF3, LF5 |
| Other Materials | Alloy 20, Monel, Inconel, Hastelloy |
| End Connections | RF, RTJ, SW, BW, NPT, FNPT |
| Bonnet Type | Bolted Bonnet, Welded Bonnet or Pressure Seal Bonnet |
Design Standard
Advantages of Pressure Seal Bonnet Check Valve
- Can handle high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- Provides a tight seal to prevent leakage.
- Requires minimal maintenance.
- Offers excellent durability and longevity.

Applications of Pressure Seal Bonnet Check Valve
Pressure seal bonnet check valves are a common choice in various industries for controlling fluid flow. In power generation, they regulate steam and fluid flow, control power output, and ensure safe and efficient operation. In the oil and gas industry, they control fluid flow during production and refining.
In chemical processing, pressure seal bonnet check valves are also widely used. They can withstand the harsh environments found in chemical plants and are ideal for controlling fluid flow throughout the production process.
Water treatment plants also rely on pressure seal bonnet check valves to control the flow of water and other fluids during the treatment process, ensuring that the water is safe for consumption.
Benefits of Pressure Seal Bonnet Check Valve
- Prevents backflow and protects downstream equipment.
- Requires no external power source.
- Reduces the risk of system damage and downtime.
- Enhances safety and regulatory compliance.
INSTALLATIONS of Pressure Seal Bonnet Check Valve
The installation of a pressure seal bonnet check valve should be done by a qualified technician. The following steps should be taken:
- Identify the correct valve size and type for your application.
- Prepare the valve and piping for installation.
- Install the valve with the proper orientation.
- Tighten the bolts to the recommended torque specifications.
- Test the valve for proper operation.
Q&A: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a pressure seal bonnet check valve? A: A pressure seal bonnet check valve is a type of check valve designed to handle high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Q: What are the advantages of using a pressure seal bonnet check valve? A: Pressure seal bonnet check valves provide a tight seal, require minimal maintenance, and offer excellent durability and longevity.
Q: What are the applications of pressure seal bonnet check valves? A: Pressure seal bonnet check valves are commonly used in power generation, oil and gas production and refining, chemical processing, water treatment plants, and petrochemical plants.
Q: How do I install a pressure seal bonnet check valve? A: The installation of a pressure seal bonnet check valve should be done by a qualified technician. It involves identifying the correct valve size and type, preparing the valve and piping for installation, installing the valve with the proper orientation, tightening the bolts to the recommended torque specifications, and testing the valve for proper operation.

- “Overview of Wedge Gate Valves: Components, Working Principle, Types, Applications, and Maintenance”
- Points To Keep In Mind When Installing Valves
- Choosing Your Pipeline: The Triple Eccentric Butterfly Valve
- Choosing Reliable Gate Valves: Types & Applications
- Different Types Of Strainers In Pipeline
- High Performance Butterfly Valve



