Understanding the Industrial Applications of Socket Welding Check Valves
Socket welding check valves play a critical role in a variety of industrial applications, ranging from the oil and gas industry to water supply, power generation, petrochemicals, and chemical admixtures. These valves are designed to prevent backflow in piping systems and are engineered to withstand extremely high pressures and temperatures. Given the importance of these valves in ensuring the safety and reliability of industrial systems, it is essential to choose the right valve for the job. In addition, regular maintenance and inspection of these valves can help to ensure their long-term performance and reliability. This can involve everything from routine cleaning and lubrication to more complex repair and replacement procedures. By working with a trusted supplier of socket welding check valves and following best practices for maintenance and inspection, industrial operators can minimize downtime, reduce costs, and ensure the safety and efficiency of their systems.
Socket Weld Check Valve Stem
Socket welding check valves operate automatically and do not require any external control or stem. Making sure to select the correct size check valve is important to avoid high pressure drops in the pipe, which can cause turbulence, chatter, and wear on the valve.
When installing a socket welding check valve, it is crucial to insert the pipe into its socket weld end with a 1/16″ gap between the pipe’s end and the bottom of the socket. This space helps prevent expansion against the fitting, leading to cracking.
Socket welding check valves typically come with either a rising stem with an outside screw and yoke or an inside screw and yoke design, which isolates the threads from the medium.

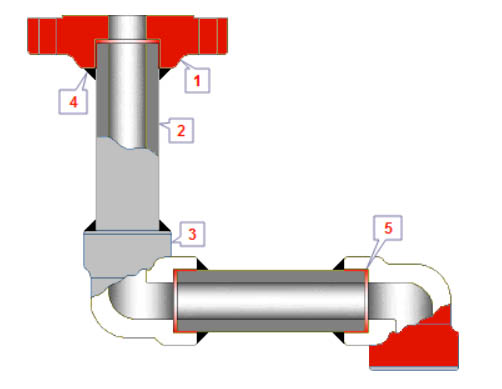
1..Socket weld flange 2..Pipe 3..Socket weld elbow 4..Fillet weld 5..Expansion gap
Socket Weld Check Valve Balls
A socket welding check valve links two pipes together to create an airtight seal. This process involves welding the two parts together for maximum security. The ball of the socket welding check valve is made from strong materials to withstand high pressure and temperature it may encounter during use. It features a handle that can be turned to open or close the valve.
The handle of the socket welding check valve is made of robust materials to withstand any torque that the operator might apply when opening or closing it. Additionally, the handle features a stem that connects it to the valve ball for added security.
Socket Weld Check Valve Packing
Socket welding is a process used to fabricate high-pressure piping systems with sealed, leak-proof joints. This involves inserting pipes into recessed sockets and fillet welding at the point where their diameter meets the sockets. When fitting pipes, it is necessary to leave a gap (usually 1/16 inch) between their end and the bottom of the socket to prevent them from bottoming out. This gap can either be manually measured and marked on the pipe with a reference line, or it can be achieved using an electronic fitment tool.
After the welding is complete, the joint is tested with water or an inert gas. Once set, the weld is hydraulically set, and dual elastomer seals activate to form an effective test boundary. Proper record-keeping is essential according to quality assurance requirements, including traceability to welding procedures, welders, materials certifications, inspections performed, inspectors’ qualifications records, and radiographs.
FAQs:
Q1. What is a socket welding check valve? A socket welding check valve is a valve that prevents reverse flow in pipelines.
Q2. What is the working principle of a socket welding check valve? The working principle of a socket welding check valve is to allow flow in one direction and prevent backflow in the other direction.
- Electric Actuated Butterfly Valve
- “Understanding the Benefits of Trunnion Ball Valves for Efficient Fluid Regulation”
- Corrosion Rate Classification Of Valve Body
- What is the Bronze Ball Valve?
- What kind of valve does the boiler generally use
- Gate Valves: Bidirectional and Versatile for Various Applications



